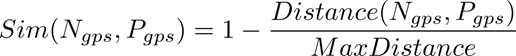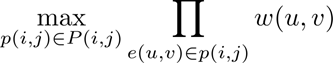|
Motivations
The Internet has witnessed the emergence
of Web 2.0 social network sites, such as Facebook and Yelp.
They allow individuals to construct a public profile and
articulate a list of connected users to traverse and share
contents within the system. They become very successful as
they bring together social experiences from across small and
disconnected off-line social networks. One the other hand,
many mobile phones also generate mobile data during its
interaction with environment, people simply use them
unconsciously to do everyday tasks and leaving record of
experience or problem about both people and the environment.
For example, a customer can comment on a meal of a
restaurant on Yelp.com with his mobile phone, which can be
viewed by other Yelp users as a reference or recommendation.
In general it is difficult for users to judge whether the
information is useful to them or not in this huge
information surge. People have to iteratively do mobile web
search, whenever they need a piece of information.
To make
people’s life better, we believe that there is a need to
proactively extract information that is of interest to
users. The project explores design of the framework
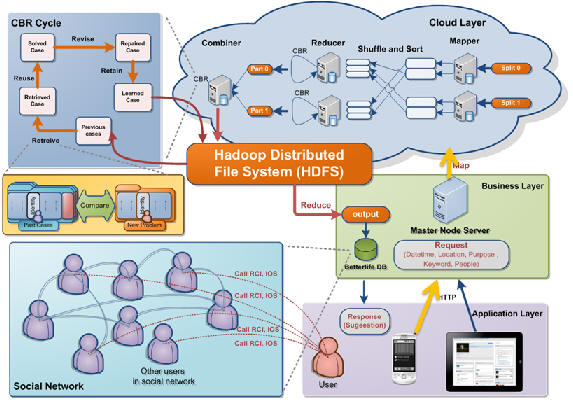
BetterLife 2.0 that implements large scale social
intelligence application on the Cloud environment. We
adopted the Case-based Reasoning framework to providing
logical reasoning. We outlined specific design
considerations when porting a typical CBR framework on Cloud
using Hadoop’s various services (e.g., MapReduce, HBases).
These services allow efficient case base management (e.g.
case insertion and adaptation) and computing intensive jobs
distribution. With the scalability merit of MapReduce, we
are able to provide recommendation service with social
network analyzing for applications that can handle millions
of users’ social activities.
Case Based Reasoning:
Case-based Reasoning (CBR) technique has been used in
context-aware recommendation systems as a reasoning technique,
which is the process of solving new problems based on the
solutions of similar past problems. Similarity-based retrieval
is a beneficial feature of case-based recommenders as it is
suitable for problems where earlier cases are available, even
when the domain is not understood well enough. With CBR,
people would benefit from a contrast-and-compare analysis by
supplying a previous case and its solution to convince a user
to make a decision.
|