POS tutorial - Preview of Windows 2000 (NT 5.0)
Brief History of Windows NT
-
32-bit preemptive mutlitaksing operating system for modern microprocessors
-
avaliable in 2 versions, Windows NT Workstation and Windows NT Server
-
1998, Microsoft decided to develop
a "new technology" (NT) portable OS that supported both OS/2 and POSIX
APIs
-
originally, NT was supposed to use the OS/2 API as its native environment,
but during development NT was changed to use the Win32 API, reflecting
the popularity of Windows 3.0
-
current version - Windows NT 4.0
-
Windows NT 5.0 - renamed to Windows 2000, to be released in late 1999
Preview of Windows 2000's new features
-
File Systems
-
Active Directory
-
NT Workstation
-
Mobile Computing
-
Security
-
Others
File Systems
-
File formats supported by Windows NT 2000
-
NTFS (NT File System), which
is the file system of NT
-
FAT, FAT32 (for compatibility
with Windows 95 OSR2 and Windows 98)
-
UDF (Universal Disk Format), which is a new file system for DVD (Digital
Video Disk) and CD media
-
Windows NT 2000's enhancements to its native NTFS format will include:
-
public key file encryption
-
distributed link tracking
-
per-user disk quotas
-
Access Control List (ACL) (this feature is already available in other OS)
NT Workstation
-
Active Desktop:
-
Microsoft Internet Explorer will be integrated into Windows NT workstation
-
Active Desktop will use Internet Explorer's familiar controls to navigate
content both on the local machine and the intranet or Internet
-
allows creation of your own interface using Active
X controls and HTML
-
Personalized Programs menu
-
Plug-and-play for detecting hardware on both desktops and laptops
Mobile Computing
-
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
-
will support power management
-
Synchronization Manager
-
will create offline copies of folders that update themselves automatically
when a mobile computer reconnects to its home network
-
Encrypted File System (EFS)
-
will let users designate files and folders to be encrypted and only accessible
with the proper public key
Active Directory
-
An entirely new directory service called Active Directory, based on the
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
-
To make network administration easier by providing a single network logon,
a single point of administration for all network objects, and the ability
to fully query the attributes of any network object
-
Backward compatible with Windows NT 4.0's directory service
Security
-
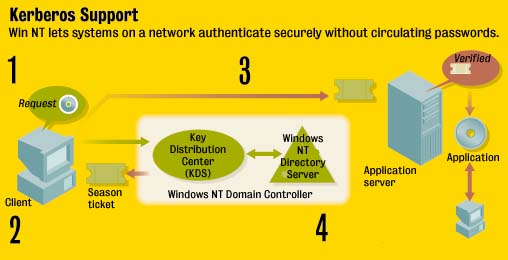
Kerberos Support - a protocol
originally developed at MIT (already being used in Unix world)
1) The client makes a request to access a program. The client authenticates
with the Windows NT Key Distribution Center (KDC).2) The KDC returns a
session ticket, which can be used for a limited period of time to authenticate
the client to network resources.
3) The client the presents the session ticket to the application server.
4) The application server verifies the ticket and gives the user access
to the requested program.
Related stories
References

