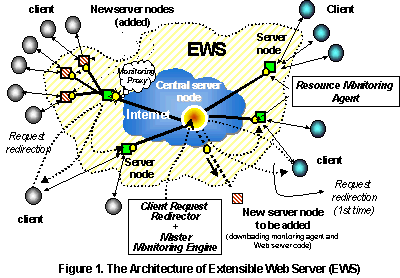
The Internet's ever-increasing popularity demands the Web sites to handle large amount of requests. This has created an urgent need for a more powerful Web server architecture to handle this problem. In this research, a distributed Web server architecture, called Extensible Web Server (EWS), is proposed. The EWS allows server nodes to be added or removed at any time. The dynamic nature of system configuration has added the challenges in the design of efficient document distribution algorithms to achieve high-performance Web services with minimum storage consumption and redirection overheads. Main features of EWS include : (1) Avoid storing unnecessary copy of document (2) Reduce the number of HTTP redirections. (3) Load Balancing.

The EWS consists of two main subsystems: (1) Resource
Monitoring Subsystem (RMS). (2) Web Service
Subsystem (WSS). The RMS is the backbone of EWS, which is used to manage the computing
and storage resources in EWS. The WSS consists of Web server software to manage the
document distribution, document consistency, document migration, and handling client
requests. Figure 1 shows an overview of the proposed EWS architecture.
Technical papers:
| Ben. Ng and C.L. Wang, “Document Distribution Algorithm for Load Balancing on an Extensible Web Server Architecture,” First IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid (CCGrid 2001), 15-18 May, 2001, Brisbane, Australia (Paper in Postscript, HTML) | |
| Ling Zhuo, Cho-Li Wang, and Francis C. M. Lau, ``Load Balancing in Distributed Web Server Systems with Partial Document Replication,'' The 2002 International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP-2002), Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, August 18-21, 2002. (Draft in PDF) |
Research Students:
| Ben NG (Graduated) | |
| Ling Zhuo (now with USC) | |
| Chen Weisong (2002, M.Phil)
|